Archive
Windows7:Enable Wired connection as primary instead of WIFI to connect in network
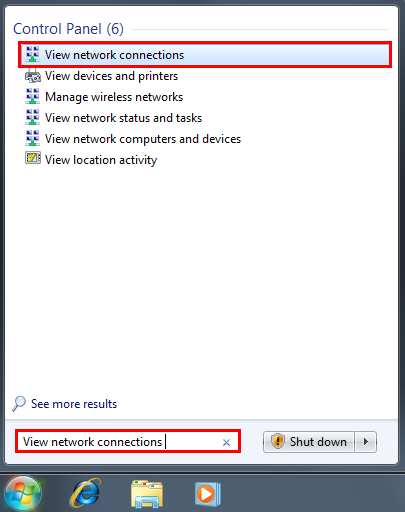
Step 1: Click Start and in the search field, type ‘View network connections’ then click to open.
Step 2: In the Network Connections screen, you will need to press the ALT key on your keyboard to get the menu bar to appear. Then click on Advanced and click on Advanced Settings.
Step 3: Now you will see the list of network connections listed in the connections box. In the Adapters and Bindings tab, click on the connection you want prioritized (eg: LAN connection) and use the up arrow to move it to the top of the list.
Click OK and now your wired connection will be the default.
Share your thoughts!
How to fix an IP address conflict?
Ever get the following message when turning on your computer or taking it out of sleep mode?
“There is an IP address conflict with another system on the network”
You may also see a different error message for the same problem:
“This IP address is already in use on the network. Please reconfigure a different IP address.”
This occurs when two computers on the same LAN network end up with the same IP address. When this occurs, both computers end up not being able to connect to network resources or perform other network
operations.
This problem, though rare, can occur because of the following reasons:
1.Two computers are assigned the same static IP addresses
2.One computer is assigned a static IP address that falls into the DHCP range for the local network and the same address is assigned to a computer by the DHCP server
3.A laptop is put into sleep mode and then turned on while connected to another network that uses the same IP address
4.If you have multiple network adapters, it is possible for a to have an IP address conflict with itself

How to resolve an IP address conflict:
There are a few ways you can go about fixing this problem. I’ll start with the simplest and move on.
1. Renew IP Address – You can release and renew the IP address for your computer using the command prompt. Read my previous post on how to renew an IP address.
2. Reconfigure Static IP Address – If your computer is using a static IP address, it is best to try and use a different one in the same subnet. One way to check to make sure the one you are picking is not already being used is to simple ping the IP addresss (ping x.x.x.x).
3. Use DHCP – If you don’t need to use a static IP address, it’s best to simply choose DHCP instead of manually configuring the IP address. The server will know which addresses are free and which are taken.
4. Update firmware – In some rare instances, the actual DHCP server can malfunction and assign more than one computer the same IP. In this case, it is best to try and update the firmware on your router.
How To Find Out What My DNS Servers Address Is?
How do I find out my DNS Server Addresses under Linux / UNIX / Windows operating system? What is my dns server IP address under Windows operating systems? Can you specify a list of public DNS server for personal use or game consoles?
DNS is key to many network services. Internet browsing, mail server, web server etc all depends upon DNS server. Most ISP (Internet service provider) have their own caching dns server to reduce network load. But how do you find out DNS server IP address? How do you find out current DNS server IP address? Under Linux, FreeBSD and all UNIX like oses you have file called /etc/resolv.conf file. It is often know as resolver configuration file. If you are using MS-Windows version Vista / 7 / NT / 2000 / XP /98 etc then see below for how to find out DNS server address under MS-Windows operating systems.
Linux / UNIX / Apple OS X Find Out Dns Server Addresses:
The resolver is a set of routines in the C library that provide access to the Internet Domain Name System (DNS). The resolver configuration file contains information that is read by the resolver routines the first time they are invoked by a process.
Commend to find out your dns servers ip address under Linux/BSD/Unixish system
To see your DNS server address type following command as shell prompt:
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
OR
$ less /etc/resolv.conf nameserver 203.54.1.20 nameserver 203.54.1.21
Where,
nameserver 203.54.1.20 : It is Name server IP address (in dot notation) of a name server that the resolver should query. All your application will use this IP address for DNS purpose.Where,
Find Out DNS Server IP Address Under MS-Windows Version 7/Vista/XP/NT/2003
Click on Start button > Run > and Type command cmd > Press [enter] key
At DOS prompt type the command:
C:\>ipconfig /all
You should DNS server IP address, and other information related to Windows networking:

OR
You can Click on Start button > Settings > Network connections
Double click on Local Area Connection
Click on Properties button
Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Click on Properties button and Look for Preferred DNS Server:

You Can Use The Public DNS Servers:
You can use the following Google public DNS (IP Addresses) servers for XBOX 360 / Sony PS3 & PS2 / Nintendo Wii game consoles or any other purpose:
8.8.8.8
8.8.4.4
They are free to all, pretty fast too and works with all sort of computers and game consoles.You Can Use The Public DNS Servers
Free DNS Server:
OpenDNS Free DNS Server IP address
=> 208.67.222.222
=> 208.67.220.220
ScrubIT Free DNS Server IP address
=> 67.138.54.100
=> 207.225.209.66
How do I setup DNS Server IP address?
Under Linux / UNIX / Solaris / BSD operating systems, just open your /etc/resolv.conf file and add above IP address:
nameserver 208.67.222.222 nameserver 208.67.220.220
What Is Attenuation?
Definition: In computer networking, attenuation is a loss of signal strength measured in decibels (dB). Attenuation occurs on networks for several reasons:
* range – both wireless and wired transmissions gradually dissipate in strength over longer reaches
* interference – on wireless networks, radio interference or physical obstructions like walls also dampen communication signals
* wire size – on wired networks, thinner wires suffer from higher (more) attenuation than thicker wires
Line Attenuation
On DSL networks, line attenuation measures signal loss between the home and the DSL provider’s access point (central exchange). Typical values for line attenuation on a DSL connection are between 5 dB and 50 dB (lower values better). Some broadband routers display these line attenuation values on their console pages, although they are typically of interest only to advanced network administrators when troubleshooting connection problems.
Attenuation in Other Contexts
The word “attenuation” sometimes applies in other environments besides computer networks. For example, professional sound mixers may use attenuation techniques to manage sound levels when blending different audio recordings together.
PAN – Personal Area Network:
Definition: A personal area network – PAN – is a computer network organized around an individual person. Personal area networks typically involve a mobile computer, a cell phone and/or a handheld computing device such as a PDA. You can use these networks to transfer files including email and calendar appointments, digital photos and music.
Personal area networks can be constructed with cables or wirelessly. USB and FireWire technologies often link together a wired PAN while wireless PANs typically use Bluetooth or sometimes infrared connections. A Bluetooth PAN is also called a piconet, and is composed of up to 8 active devices in a master-slave relationship (a very large number of devices can be connected in “parked” mode). The first Bluetooth device in the piconet is the master, and all other devices are slaves that communicate with the master. A piconet typically has a range of 10 meters, although ranges of up to 100 meters can be reached under ideal circumstances.
Personal area networks generally cover a range of less than 10 meters (about 30 feet).